How routing works in Networking Hubs
When using Networking Hubs, much of your routing requirements will be configured by default. These default configurations can be discovered by reviewing the resources created in AWS, or visually using the concepts displayed in this document. To modify these routing configurations, consider utilizing advanced routing.
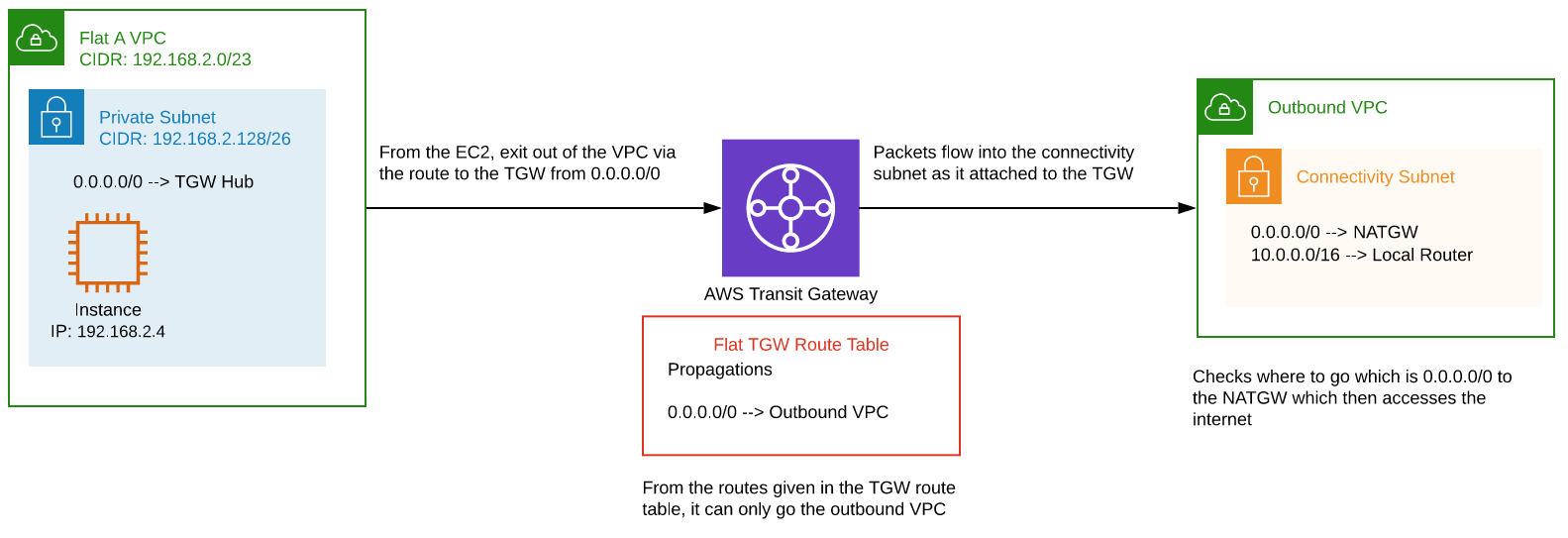
VPC to centralized egress
Pinging an internet IP from an EC2 instance in the private subnet of a flat VPC.
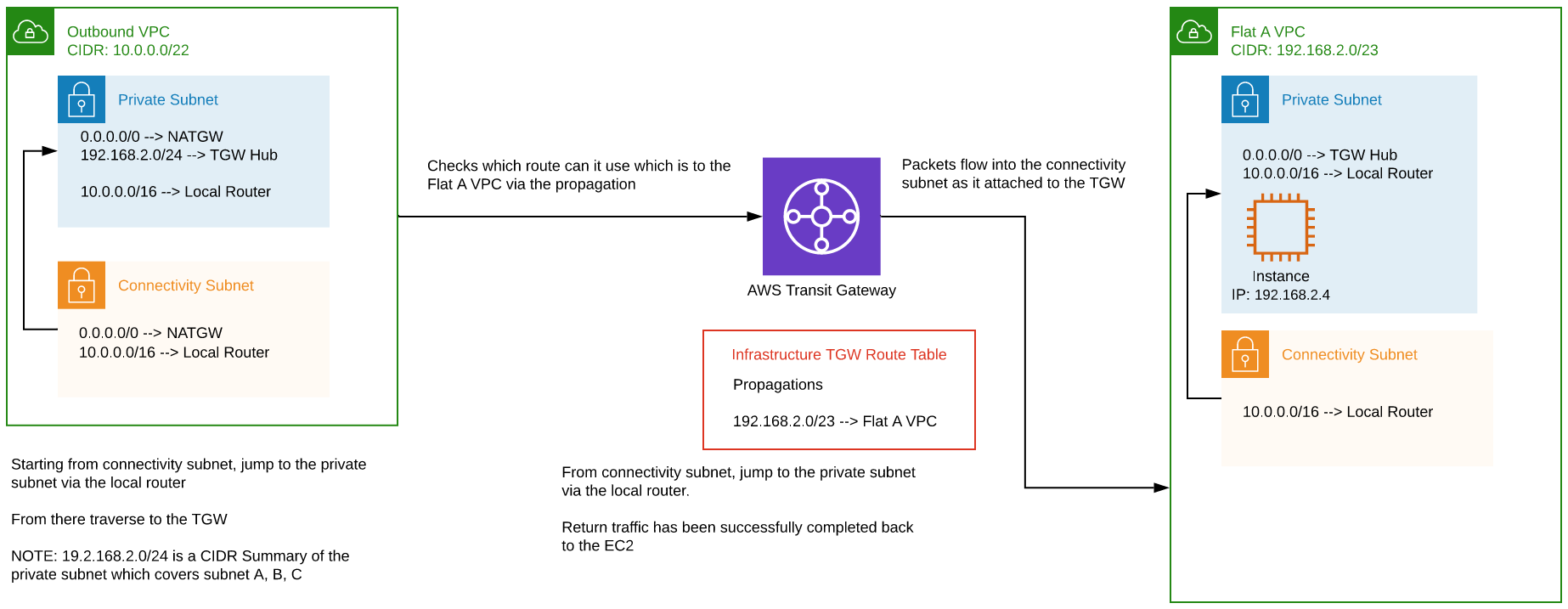
VPC to centralized egress return traffic
Traffic must return to the EC2 instance in the flat VPC.
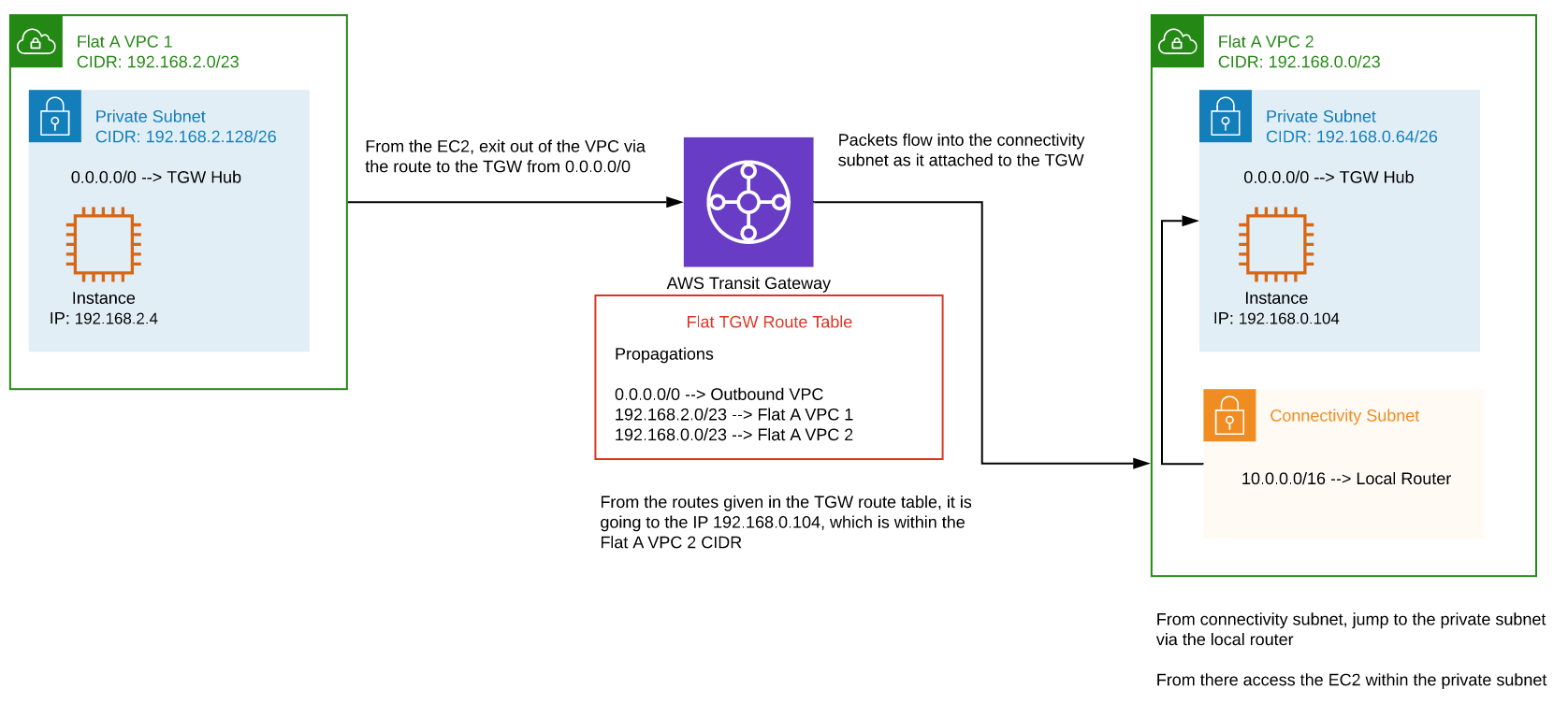
VPC to VPC (inter-zone)
Connecting an EC2 instance (192.168.2.4) in a flat VPC to an EC2 instance (192.168.0.104) in a flat VPC within the same zone.
VPC to VPC (inter-zone) return traffic
Traffic must return back to the EC2 instance in the flat VPC.
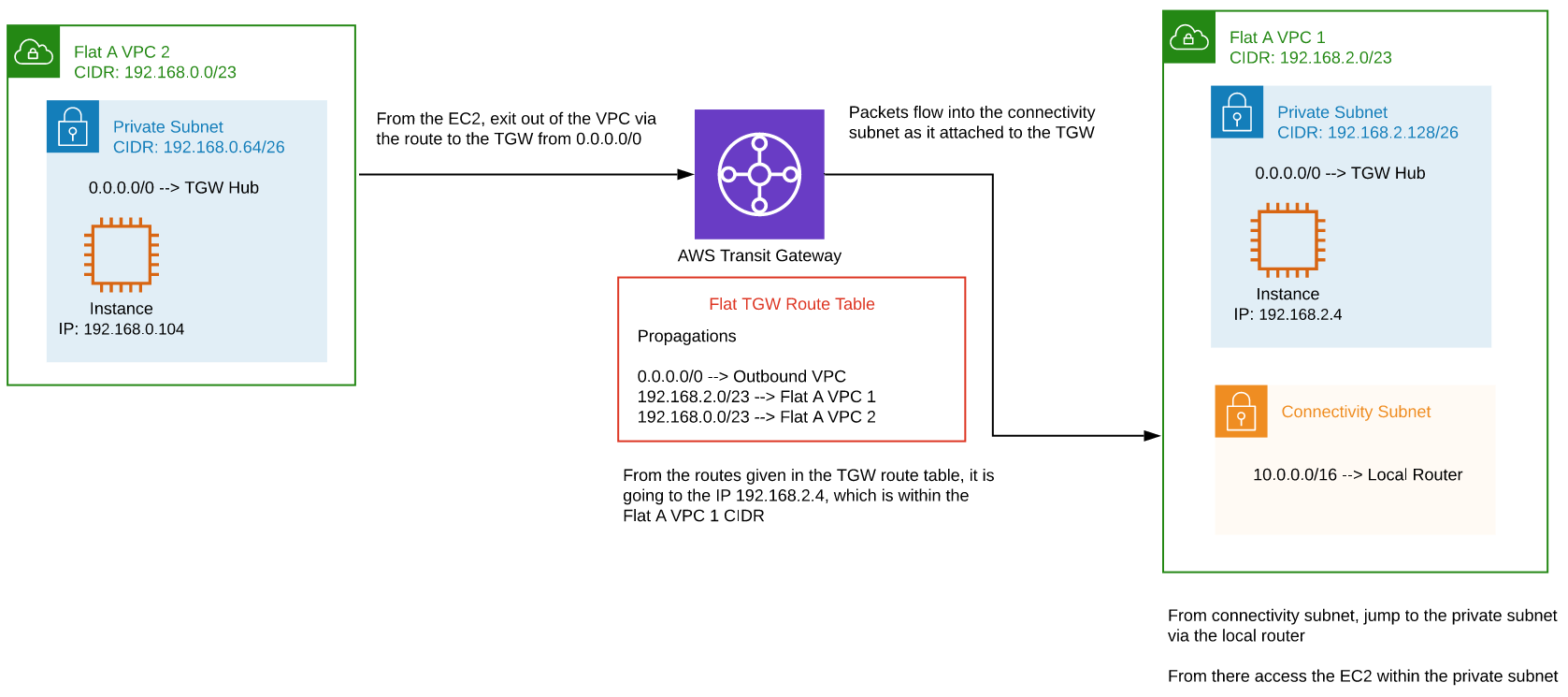
VPC to VPC (zone to isolated)
Connecting an EC2 instance (192.168.2.4) in a flat VPC to an EC2 instance (192.168.4.168) in an isolated VPC.
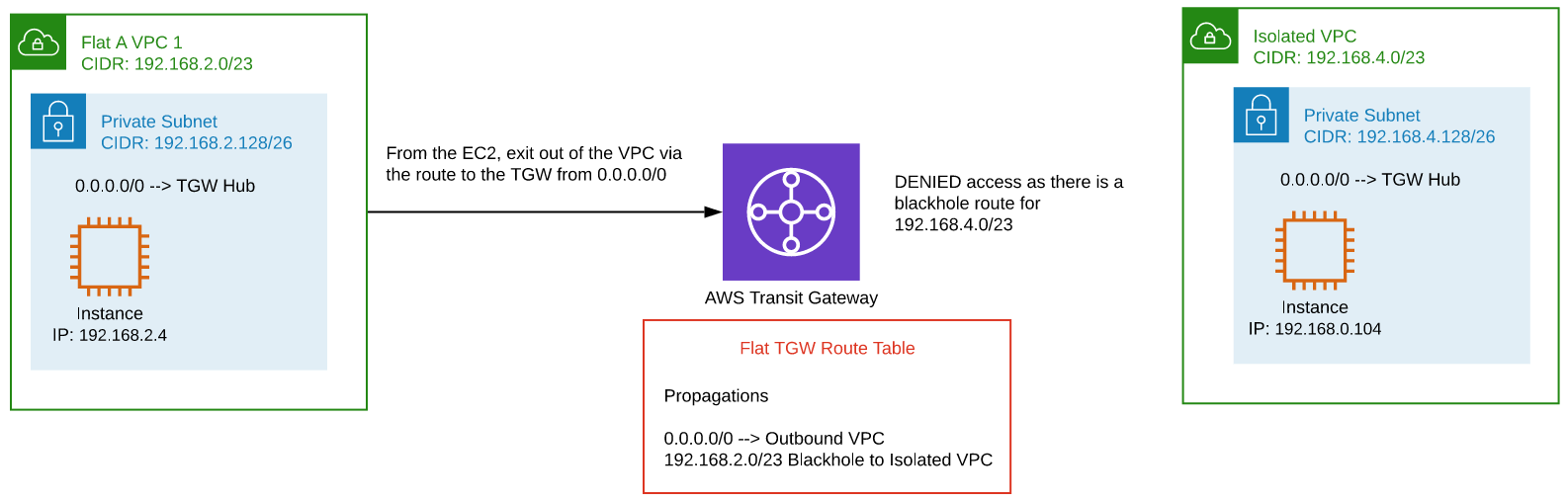
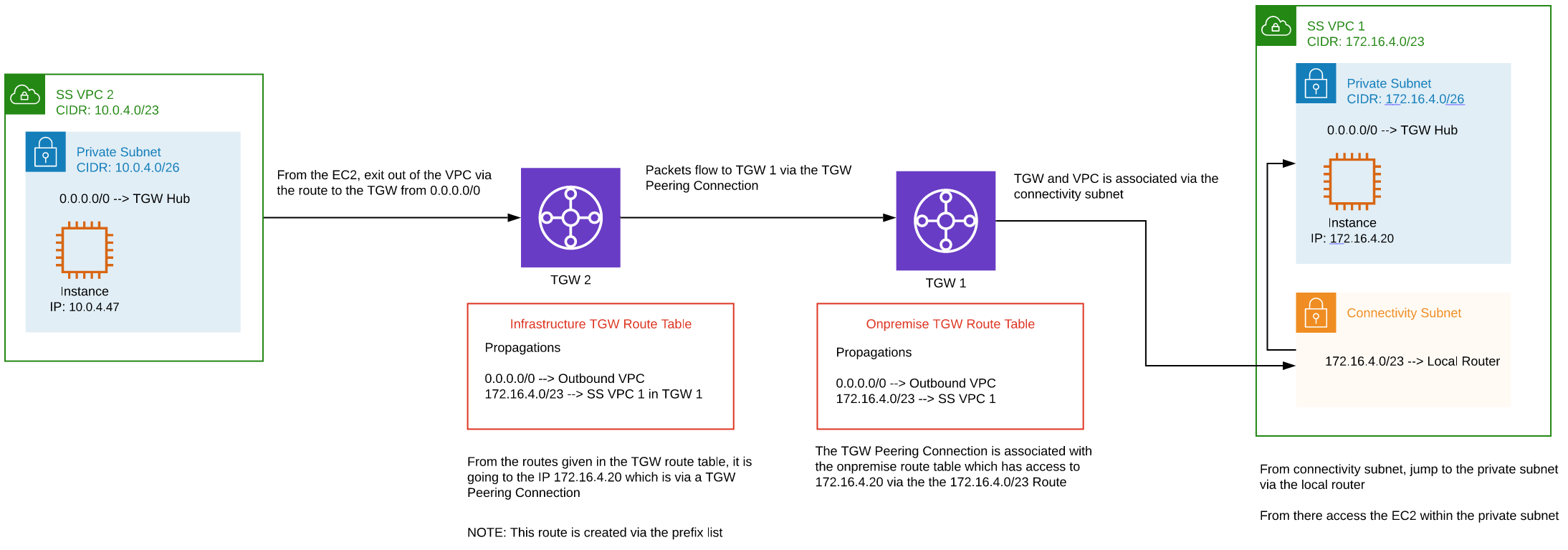
VPC to VPC (peered Networking Hubs)
Connecting an EC2 instance (172.16.4.20) in a shared services VPC to an EC2 instance (10.0.4.47) in a shared services VPC in another Networking Hub connected using Hub Peering.
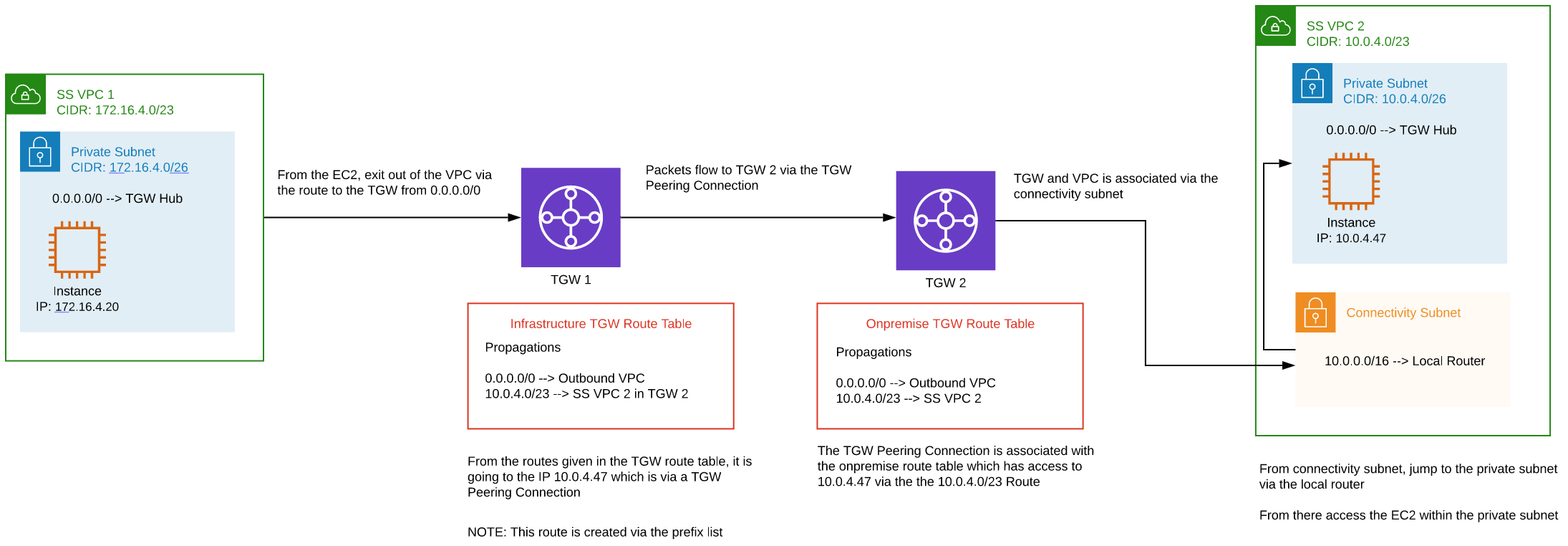
VPC to VPC (peered Networking Hubs) return traffic