Understanding Financial Mode
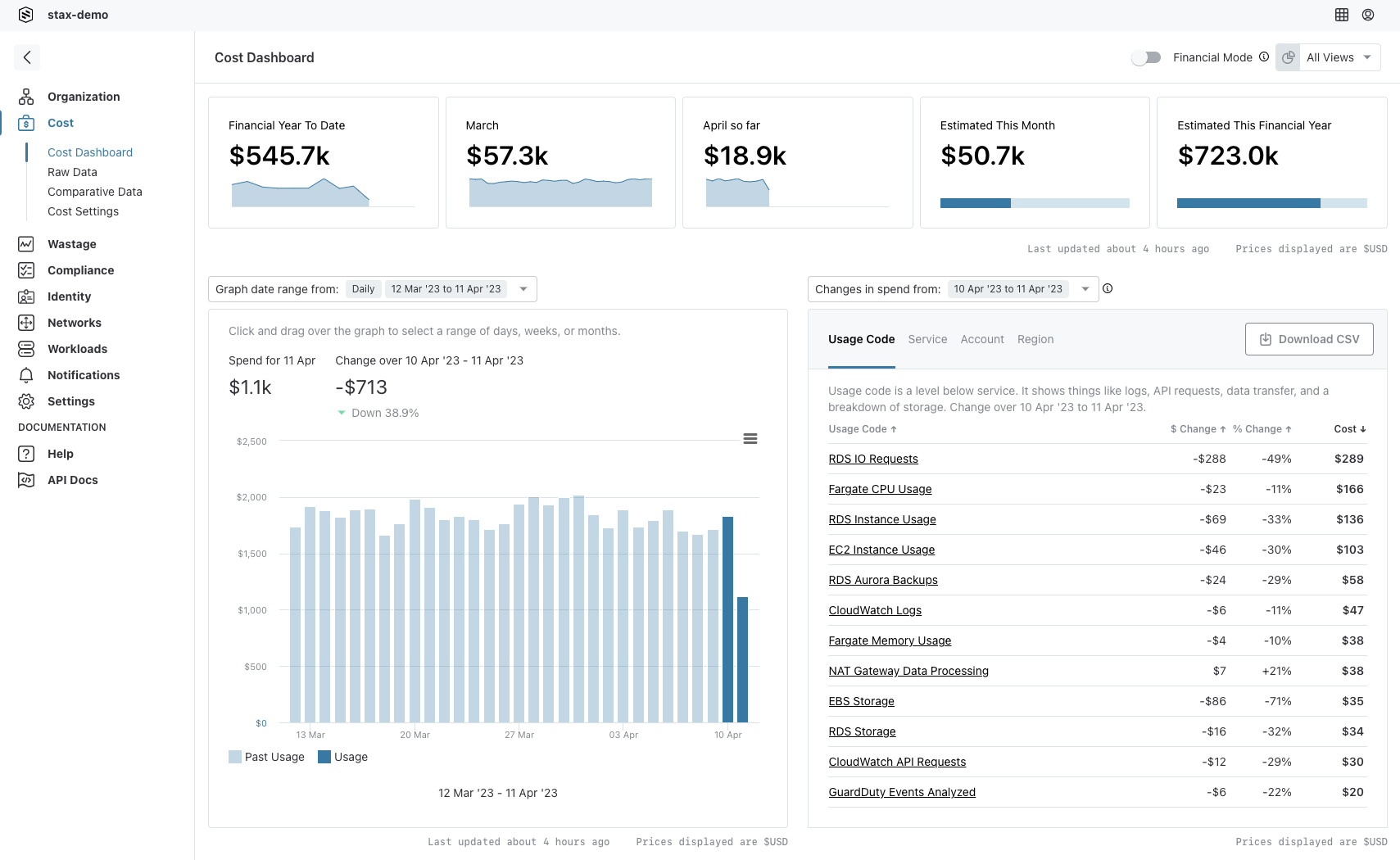
The default view in Stax, known as Usage Mode, shows usage information. This is calculated based on the overall consumption of AWS resources, and does not take into account any discounts, credits, support charges, or other factors that may be applied to your bill. From a detailed bill standpoint, Usage Mode shows only the usage amount, that is, billing items where the kind is usage.
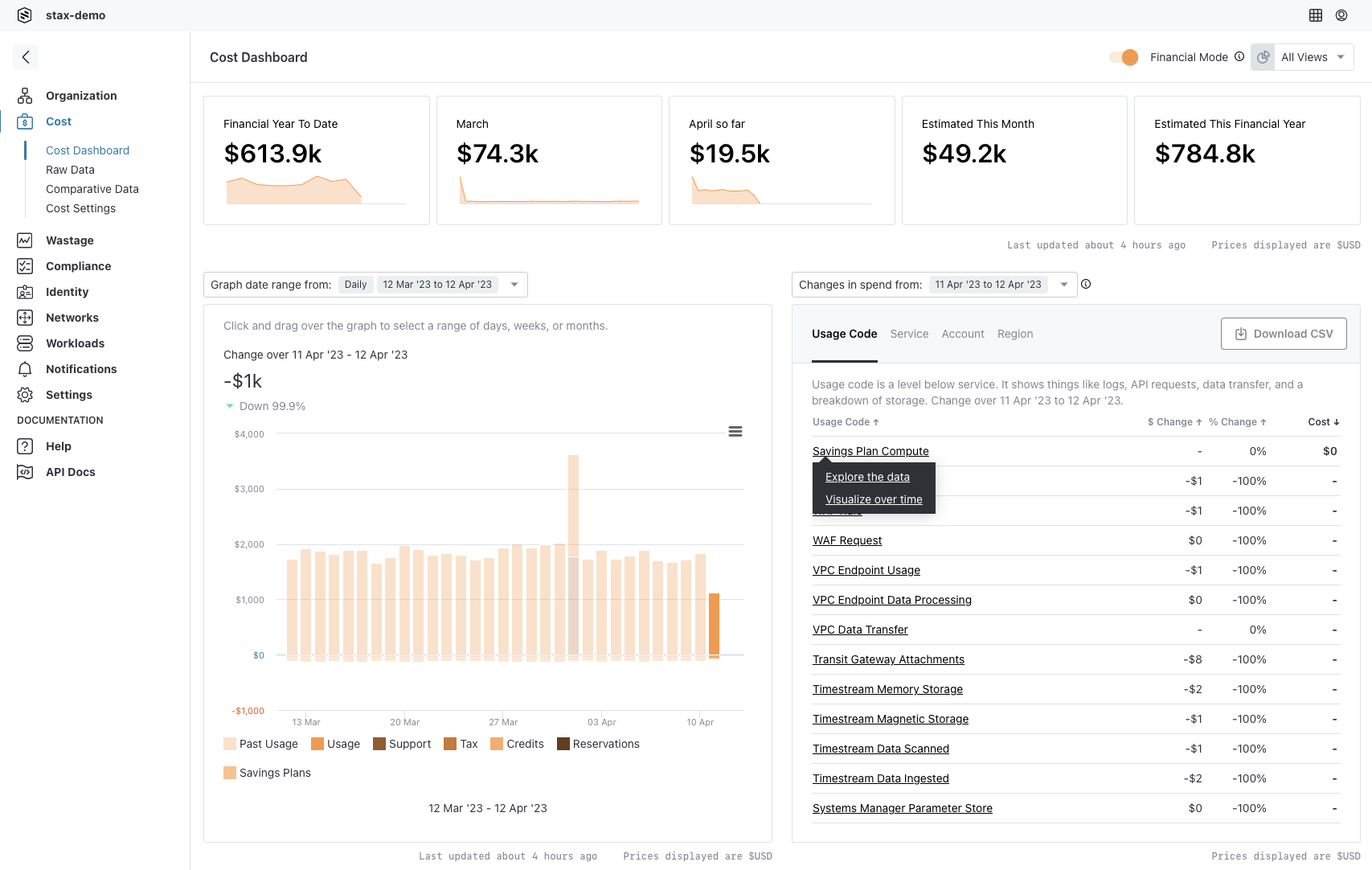
Stax offers another option on the Cost page: Financial Mode. Financial mode shows all billing items, including tax, credits, support charges, and more. It shows the unblended cost for each billing item.
Enable Financial Mode
To enable Financial Mode in Stax, on the Cost page of the Stax Console, simply toggle the Financial Mode switch:
Usage Mode
Financial Mode
Cost Metrics
Stax refers to the two types of visible costs, either usage cost or unblended cost, as the current cost metric. On the Data page, the Total Usage Cost represents the usage cost (or "amortized cost") cost metric. The term "unblended cost" is an AWS billing term, Stax represents it as the financial cost cost metric.
Stax defines the "Amortized cost" you see in Usage Mode as the first value of the following:
- Savings Plan Effective Cost
- Reservation Effective Cost
- Unblended Cost
This is important because of the way costs are applied:
- Reservations apply by changing the unblended rate on a billing record to a lower value, and then adding new billing record (with the value of kind being "reservation") with the extra cost shown. For example, with a full upfront reservation, the usage for an EC2 billing record will drop to $0, but an additional billing record will exist for the upfront cost of the reservation.
- Savings Plans work by keeping the original billing record with the actual usage cost, but adding an appropriate discount. For example, a billing record for an EC2 instance with an hourly cost of $0.20 might be accompanied by an additional billing record providing a $0.05 discount per hour. The net cost for this example resource would be considered to be $0.15 per hour
Most services which don't support either reservations or Savings Plans simply use the unblended cost, which is default value for Stax's usage cost cost metric.
Effective Costs
Savings Plan Effective Cost is a view on a billing record where kind equals "usage". Following on from the example above where a $0.20 billing record might have an accompanying $0.05 discount, resulting in a Savings Plan Effective Cost of $0.15.
Reservation Effective Cost works similarly, taking into account upfront cost and amortizing it into an effective cost.
With Stax's Usage Mode enabled, you will see a figure that amortizes the Savings Plans and Reservation costs. Whether using Stax's Usage Mode, or the Data page's "Total Usage Cost" column, it will represent the cost of usage.
With Financial Mode enabled, Stax performs little processing of the cost data itself. The broken out, processed data from the billing report is shown. Discounts from Savings Plans (kind is "credit" and payment_option_code is "savings_plan") and reservation usage costs (kind is "reservation") will be separated.
On the Data page, grouping by "Kind" will show the Sum of Financial Cost column. This will equal what is represented on the AWS bill. The Sum of Usage Cost will not necessarily be suitable, as it shows both discounts and added costs amortized into the usage cost for each billing record.
Considerations
A side effect of the usage cost metric using the effective cost values from Amazon's Cost and Usage Report is that costs can be moved around accounts. This can occur when AWS applies Savings Plans. This can result in representing financial costs that are not present in the current month.
Using the Data Page
On the Data page you can view and filter all kinds of billing records.
Usage Mode is equivalent to filtering to show only records where kind is "usage", and then grouping by "kind". The values in the Total Usage Cost will match those of Usage Mode.
Financial Mode is equivalent to grouping by "kind" with no filter. The values in the Total Financial Cost column will match those of Financial Mode.